Differentiation of cells and diversity of plant tissues
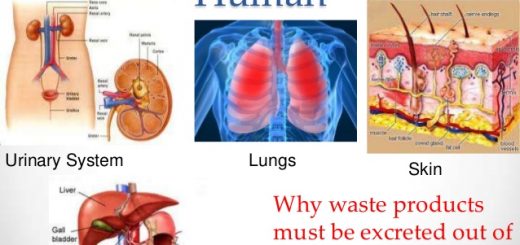
The human body is composed of many systems integrate together forming the body of the living organism, such as the circulatory, nervous, digestive, respiratory, excretory, and reproductive systems.
Organization of living organisms
We will take the human as an example of multicellular living organisms to identify his body building, The system is composed of a group of organs work together, such as the circulatory system which consists of the heart , blood and blood vessels.
The organ is composed of a group of tissues organized together to perform certain functions, such as the heart which consists of a cardiac muscular tissue, nervous tissue and connective tissue that collaborate together to pump the blood from the heart to all body parts.
The tissue is composed of a group of cells specialized in their work and if these cells forming the tissue are symmetrical with each other in the structure , shape and function , the tissue is called simple tissue and if there are more than one type of cells , the tissue is called compound tissue .
Simple tissue consists of only one type of cells that similar in structure , shape and function , Compound tissue consists of more than one type of cells .
Tissues are varied depending on the difference and diversity of living organisms , vital activities and functions they perform .
Human body consists of many systems that consist of many organs , The organs consist of many tissues , The tissues consist of many cells .
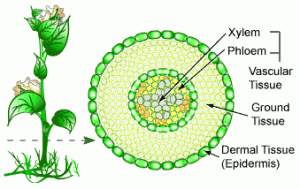
Plant tissues
Plant tissues can be differentiated into simple and compound tissues , Simple tissues such as ( Collenchyma tissue , Parenchyma tissue and Sclerenchyma tissue ) , Compound tissues such as Conductive tissues ( Xylem tissue and phloem tissue ) .
Simple tissues
Parenchyma tissue
Functions : Do photosynthesis , Store nutrients such as starch and responsible for aeration, It is a living tissue , its cells are characterized by the following :
Oval or rounded shaped , Their walls are thin and elastic , There are spaces ( intercellular spaces ) between them for aeration , It contains chloroplasts , chromoplasts or leucoplasts , It contains one big vacuole or more filled with water and mineral salts .
Collenchyma tissue
It is a living tissue , its cells are characterized by the following : Somewhat rectangular shaped , Their walls irregularly thickened with cellulose .
Function : Supporting the plant by acquiring it a suitable elasticity .
Sclerenchyma tissue
It is a non-living tissue , its cells are characterized by : their walls are thickened by lignin substance in addition to cellulose and solid tissue .
Functions : Strengthening and supporting the plant by acquiring it the hardness and elasticity .
Compound tissues
Xylem tissue
Structure : It consists of vessels , tracheids and parenchyma cells , The vessels are tubes , each of them is made up of a vertical row of cells , where : protoplasm and transverse walls were disappeared , Lignin substance was deposited on inner surface of their walls at the inside .
So, these cells are converted into long wide vessels transporting the water and salts, their length ranges from few centimetres to several metres as in high trees.
The tracheids : Each of them is composed of one cell , where protoplasm disappeared from it , Their walls get lignified .
Functions : Supporting the plant, Transporting the water and salts from the root to the stem and leaves.
Phloem tissue
Structure : It consists of sieve tubes and companion cells .
The sieve tubes originate from compact cells , vertically above each other , where : Their nuclei disappeared , Their separating walls became perforated ( So , they are called sieve plates ) through which cytoplasm passes in the form of cytoplasmic strands .
The companion cells are living cells located adjacent to the sieve tubes to provide them with the energy they required to perform their function.
Function: Transporting the nutrients resulted in photosynthesis from the leaves to the other plant parts.
Excretion in plants, Importance & types of transpiration for the plant
Transportation in plant, Structure & role of the plant stem in the process of transportation
Histology, Molecular structure of the cell membrane, Cell function & structure












Excellent information. Very useful site.
Thank you very much for your comment