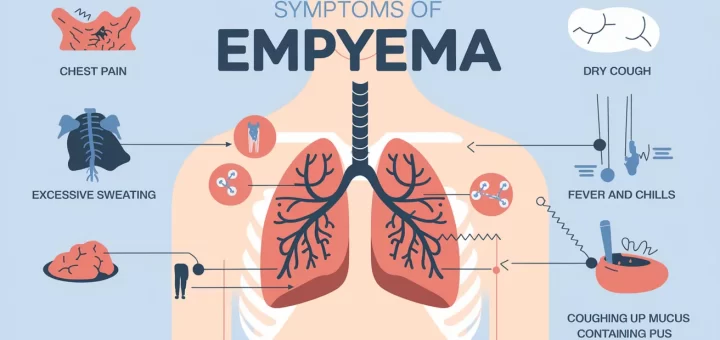
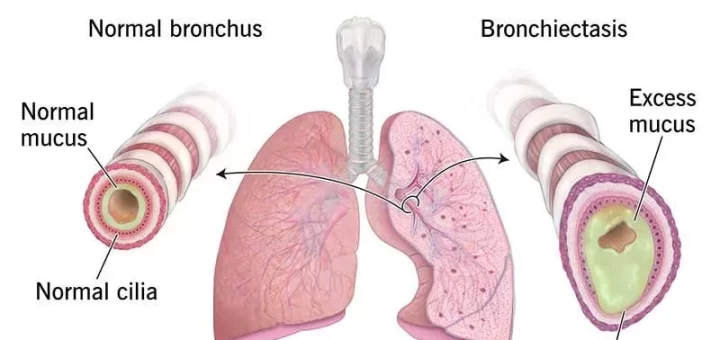
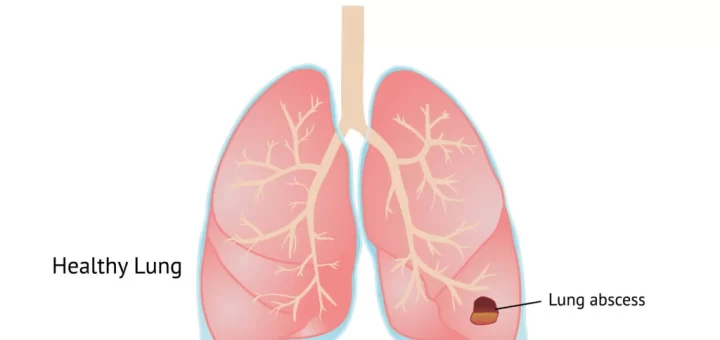
Pleural disease symptoms and treatment, What is the most common pleural disease?
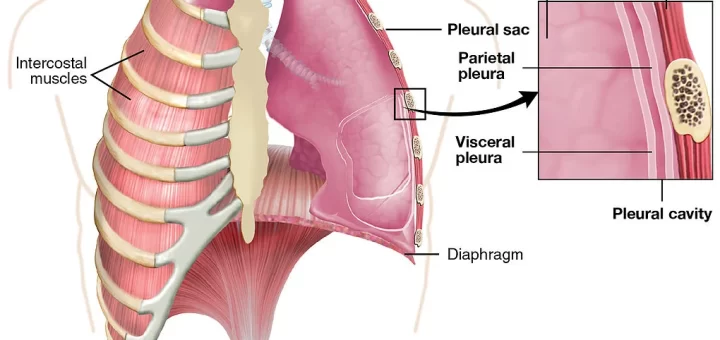
Pleural diseases are conditions that affect the pleura, which is the thin membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the chest cavity. The pleura consists of two layers: the visceral pleura (which covers the lungs)...