What are the factors affecting the weight?
The weight
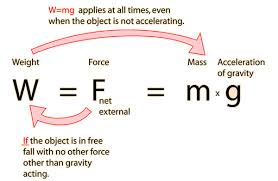
The reason of object’s falling downward the Earth is a type of force called the weight (the gravitational force), and you can feel this force when you carry an object or try lifting it, The weight is the force with which a body is attached to the Earth or it is the gravitational force by which a body is attached to the Earth.
The effect of the weight is always directed towards the center of the Earth, On Earth, all the objects have the weight, but in space, all the objects are in a state of the weightlessness, The weight of any object can be measured by the spring scale by determining the extension of its spring.
Everything seems weightless inside the spacecraft which revolves around the Earth, Newton is the measuring unit of the weight and it is almost equal to the weight of an object on the Earth’s surface whose mass is 100 grams.
The factors affecting the weight
The weight of any object is affected by three factors which are the object’s mass, the planet (the place) where the object exists, the distance between the object and the center of the planet.
The weight of any object on the Earth’s surface increases by increasing the object’s mass, The weight of an object differs according to the planet (or the moon) where the object exists.
As the mass of the planet (place) increases. its gravitational force for an object increases, So the weight of the object increases.
The weight of the object on the moon’s surface equals one-sixths of its weight on the Earth’s surface because Earth has greater mass and gravitational force than the moon.
The weight of anybody decreases when the distance between the body and the center of the planet increases because the gravitational force decreases.
The gravity and the weightlessness in the solar system
The properties and the measuring devices of the mass
The scalar physical quantity and vector physical quantity
The types of speed and the factors necessary for the description of motion