Power Potential of hydrogen (hydrogen ion concentration) pH, Relation between pH & enzyme activity
Power Potential of hydrogen
It is a measurement determining the concentration of hydrogen ion (H+) in the solution and whether the solution is basic, acidic or neutral, You can determine pH of any solution by using the pH indicators, The acid is the substance that can give up a hydrogen ion (H+) and the base is the substance that can accept H+.
If the potential of hydrogen ( pH ) is :
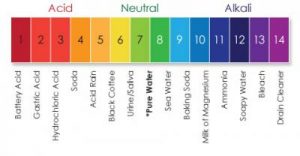
- Less than 7 , the solution is acidic ( pH < 7 ) .
- Greater than 7 , the solution is basic ( pH > 7 ) .
- Equals 7 , the solution is neutral ( pH = 7 ) .
The neutral potential of hydrogen ( pH = 7 ) equals pH of pure water at 25 degree Celsius , The values of power of hydrogen of solutions are ranged between ( Zero : 14 ) depending on their positive hydrogen ion concentration (H+) .
pH is the numeric scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of the aqueous solution , It is the negative of logarithm to base 10 of the molar concentration , It is measured in units of moles per liter of hydrogen ions , It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion .
The solutions with the pH less than 7 are acidic and the solutions with the pH greater than 7 are basic , The pure water is neutral , being neither an acid nor a base , The pH value can be smaller than 0 or bigger than 14 for strong acids and bases .
The pH measurements are important in the agronomy , the medicine , the biology , the chemistry , the agriculture , the forestry , the food science , environmental science , oceanography , civil engineering , chemical engineering , nutrition , the water treatment and the water purification , as well as many other applications .
The pH scale is traceable to the set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement , The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with the glass electrode and the pH meter , or the indicator .
The primary pH standard values are determined using the concentration cell with transference , by measuring the potential difference between the hydrogen electrode and the standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode .
PH in the human body
The pH is used as the measure of whether the body is maintaining the normal acid-base balance , The favorable pH is important in the function of the enzymes and the other biochemical systems , The fluids of the body are normally somewhat alkaline , The pH being between 7.35 and 7.45 , The pH above 7.8 or below 6.8 is generally fatal .
The symbol for the negative logarithm of the H+ ion concentration ( measured in moles per liter) , The solution with pH 7.00 is neutral at 22°C , one with the pH of more than 7.0 is alkaline , and one with the pH lower than 7.00 is acid , At the temperature of 37°C , neutrality is at a pH value of 6.8 .
The measurement of the acidity or the alkalinity of the solution based on the amount of hydrogen ions available , Based on the scale of 14 , The pH of 7.0 is neutral , The pH below 7.0 is an acid , the lower the number, the stronger the acid , The pH above 7.0 is the base , when the number is higher , The base is the stronger , Blood pH is slightly alkaline (basic) with the normal range of 7.36-7.44 .
Relation between pH and enzyme activity
Enzymes are affected by changing pH values because they are protein substances that contain acidic carboxyl groups ( COOH ) and Basic amino group ( NH2 ) , Each enzyme has an optimal pH value at which it works with a maximum efficiency .
If the pH is lower or higher than the optimal pH of the enzyme , The enzyme activity decreases until it stops working , Optimal pH of enzyme is the potential of hydrogen ( pH ) at which the enzyme works with a maximum efficiency .
Examples
- Pepsin works at acidic pH value
- Trypsin works at basic pH value .
Most enzymes work at pH value equals 7.4 ( neutral medium ) due to the amino acid molecules that forming the enzyme contain an acidic carboxyl group and a basic amino group .
Nanobiopharmaceuticals
They are biological macromolecules ( proteins ) that are produced and used in treating some diseases in the human body .
Disadvantages
It is difficult to carry on the medicine directly to the target parts or cells in the body like several medicines .
The method to avoid these disadvantages
After the enormous development resulted by the nanotechnology , many trials are conducted to carry on the medicine to the infected cells in the body using nanoparasites .
These trials have led to the arising of a new field called nanobiopharmaceutics and the products used in this field are called nanobiopharmaceuticals .