The asexual reproduction by tubers in plants
Reproduction by tubers
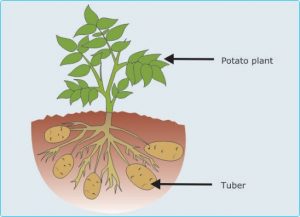
The tuber is a horizontal root or a terrestrial stem or which contains growing buds and it is used for the vegetative reproduction, It is root as the sweet potatoes, and it is a stem as the potatoes.
The tubers are various types of modified plant structures that are enlarged to store the nutrients, they are used to provide the energy and the nutrients for regrowth during the next growing season, and they are used by the plants to survive in the winter or dry months.
The tubers are enlarged, fleshy underground stems such as the potatoes, The stem tuber forms from thickened rhizomes or stolons, Some buds in the tuber grow forming the shoot system that grows into the typical stems and leaves above the soil.
The other buds in the tubers grow to form the root system that buried inside the soil, The offspring or the new tubers are attached to the parent tuber, and in the autumn the plant dies except for the new offspring stem tubers which have one dominant bud.
In the spring, The tuber regrows a new shoot producing the stems and the leaves, in summer the tubers decay and the new tubers begin to grow.
Most gardeners plant seed potatoes which are the pieces of potato that have at least two or three buds, As the plant grows, It uses the food reserves in the seed, The potatoes are stem tubers that enlarged stolons thicken to develop into the storage organs.
The stem tubers are swollen underground stems, with reduced scale leaves and axillary buds, They are distinct from the rhizomes because their terminal shoot apex stops growing and development is entirely radial and lateral.
The potato is a starch-accumulating tuberous plant, and the tubers do not contain chlorophyll unless exposed to the light, The tuberous stems are swollen sections of the stem, they don’t occur at the tips of underground stems, and they occur on the main stem.
The tuberous stems have a vertical orientation with the vegetative buds which produced on the upper end, The tuberous stems are perennial, and continue to enlarge every year.
The production of the tubers is one way that a plant can store the carbohydrates during the growing season, Then at the end of the growing season, The above-ground portion of the plant dies back, The new tubers overwinter, and sprout again in the spring.
The root tubers resemble the stem tubers such as the sweet potatoes, they are fleshy swollen roots and store reserves such as the starch, The tuberous roots are enlarged secondary roots as they are the root tissue, There are no nodes or buds, and two familiar examples of plants with tuberous roots are the sweet potato and dahlia.
Excretion in plants, Importance & types of transpiration for the plant