Skeletal system, Axial skeleton (vertebral column, Skull and thoracic cage)
The skeletal system in man works on supporting the body, protecting some of its organs and participating in the movement in addition to providing the man with his special shape, Skeletal system in man consists of skeleton, cartilages, joints, ligaments & tendons.
Skeleton
The skeleton in man consists of 206 bones, where each bone has a shape and size that are suitable for its function.
Structure of the skeleton:
- The axial skeleton consists of a vertebral column, skull, and thoracic cage.
- The appendicular skeleton consists of (pectoral girdle and upper limbs), (pelvic girdle and lower limbs)
The axial skeleton
Vertebral column
The vertebral column is considered as the axis of the skeleton, where its upper part is attached with the skull, At the thoracic region, it is attached with the thoracic cage and upper limbs by the pectoral girdle, Its lower part is attached with the lower limbs by the pelvic girdle.
It consists of 33 vertebrae that are divided into 5 groups and differ in shape according to the site of their presence as follows:
- 7 cervical vertebrae: articulating and has moderate size.
- 12 thoracic vertebrae: articulating and larger than the cervical vertebrae in size.
- 5 lumbar vertebrae: articulating and the largest of all vertebrae in size (found in the abdominal region).
- 5 sacral vertebrae: broad, flat and fused.
- 4 coccygeal vertebrae: small and fused.
The number of bones of vertebrae column in human is about 26 bones, The structure of bony vertebra consists of several parts which are:
- The centrum is the anterior thick part.
- The two transverse processes are two bony processes that attached laterally with the centrum and each one of them carries an articulating anterior bony process.
- The neutral ring is a bony ring that is attached posteriorly with the centrum and surrounds the neutral canal inside which the spinal cord extends to protect it.
- The neutral spine is a posterior bony process that is directed downwards, carried by the neutral ring and carries two posterior articulating processes.
The function of the vertebral column: it acts as the main support of the body, It protects the spinal cord, It helps in the movement of the head and upper body parts.
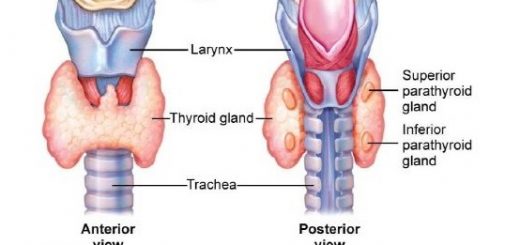
The skull
It is a bony case that consists of two parts which are:
- Posterior part (Cerebral part): It consists of 8 serrated bones that are attached firmly to each other to form a cavity that encloses the brain to protect it, At the base, there is a foramen magnum through which the spinal cord is attached to the brain.
- Anterior part (Facial part): It includes the face bones, two jaws and the positions of sense organs (eyes, ears & nose).
Thoracic cage
A case that is slightly conical in shape attached posteriorly to the thoracic vertebrae (12 vertebrae) and anteriorly to the sternum bone.
The thoracic cage consists of twelve pairs of ribs which are as follows:
First ten pairs: attached between the thoracic vertebrae and sternum bone.
The two lower pairs of ribs (pairs no. (11) and (12): are short and do not reach the sternum, So, they are called the floating ribs and they are attached to the vertebrae no. (18) and (19) of the vertebral column.
The rib is a curved bone that bends downwards and attached posteriorly to the centrum of the thoracic vertebra and its transverse process, The sternum is a flat bone that is pointed at its lower part which is cartilaginous and to which the first ten pairs of ribs are attached.
The function of the thoracic cage: It protects the heart and two lungs, It helps the ribs movement during the respiration process, where: during the inspiration process, the ribs move anteriorly and laterally to increase the volume of the thoracic cavity, during the expiration process, the ribs move opposite to what was done in the inspiration process.
Bones function, types & structure, The skeleton & Curvature of Spine in Adults
Skeletal system, Appendicular skeleton structure and importance
Skeletal system, Importance of Cartilages, Joints, Ligaments & Tendons