Atomic emission spectra, Bohr’s atomic theory and Wave mechanical theory of the atom
On heating atoms of pure elements – in a gaseous or vapor state – to a high temperature or exposing them to low pressure in an electrical discharge tube, they emit a radiation called emission spectrum ( line spectrum ).
Atomic emission spectra
On examining this radiant light with a device called a spectroscope, it was found that it is composed of a limited number of restricted colored lines separated by dark areas, So, it is called a line spectrum, It is worth mentioning that the physicists – at that time – were not able to explain this phenomenon.
A line spectrum is a type of spectrum composed of a small number of restricted coloured lines separated by dark areas, The radiant light is named a line spectrum because it is composed of a limited number of restricted coloured lines which are separated by dark areas.
Application: The line spectrum of the hydrogen atom appears (on examining) as four coloured lines separated by dark areas, It was found experimentally that the spectral lines are essential characteristics for each element because there are no two elements that have the same spectral lines.
Bohr’s atomic model (1913)
The study of atomic spectra is considered the key that solved the puzzle of the atomic structure, That was the work of the Danish scientist Niels Bohr upon which he was rewarded the Nobel Prize in 1922.
Bohr’s Postulates
Points that agree with Rutherford’s postulates
- A positively charged nucleus exists in the center of the atom.
- The number of negative electrons (revolving around the nucleus) equals the number of positive protons inside the nucleus.
- During the revolving of the electron around the nucleus, a centrifugal force arises which is equal to the attraction force of the nucleus on the electron.
New postulates
Electrons orbit the nucleus in a rapid movement without emission or absorption of any amount of energy and the atom in this case named a stable atom.
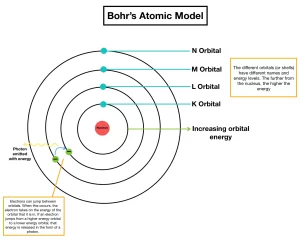
Electrons orbit the nucleus in definite allowed energy levels, They can not be found at intermediate distances, at which electron moves from one energy level to another via a complete jumping.
Each electron in the atom has a definite amount of energy depending on the distance between its energy level and the nucleus, the energy of any level increases as its radius increases, Each energy level is expressed by a whole number called the principal quantum number (n).
When the electron acquires a quantity of energy – known as quantum – by heating or by electric discharge, the electron jumps temporarily to a higher energy level, This is in case that the absorbed quantum of energy is equal to the difference in energies between the two levels, and the atom is known as an excited atom.
Since the electron in the excited atom is unstable, it returns to its original level with emission of the same quantum of energy (emission spectrum) in the form of radiant light that appears in the form of characteristic spectral lines of a certain wavelength and frequency.
Quantum is the amount of energy absorbed or emitted, when an electron is transferred (jumps) from one energy level to another, An Excited atom is an atom that acquires an amount of energy by heating or by electric discharge.
The multitude of atoms absorb different amounts of energy, and then radiate their energies producing spectral lines, These spectral lines correspond to the energy levels from which their electrons are transmitted back to the ground state.
The spectral line of the hydrogen atom does not represent the electron transferring from :
- The different energy levels to the first energy level, because the wavelength of the emitted ray from the excited electron is located in the invisible region of the ultraviolet rays.
- The seventh energy level to the second energy level, because the wavelength of the emitted ray from the excited electron is located in the invisible region of the infrared rays.
The quantum of energy required to transfer an electron between the different energy levels is not equal, One quantum is the energy difference between the two energy levels.
An electron can’t move from its energy level to another if the energy absorbed or emitted is less than one quantum, (there is a half quantum for instance).
The quantum of energy required to transfer an electron between the different energy levels is not equal, because the distance and the difference in energy between them are not equal.
The quantum of energy required to transfer an electron from one energy level to another decreases as we go further from the nucleus, Because the energy gap decreases, as we go further from the nucleus.
Advantages & disadvantages of Bohr’s atomic model
Despite of the great effort of Bohr to construct his atomic model, the quantitative calculations of his theory did not agree with all the experimental results.
Advantages (success) of Bohr’s atomic model:
- It explained the hydrogen atom spectrum.
- It introduced the idea of quantized energy to determine the electron energy in different energy levels in the atom.
Inadequacies of Bohr’s atomic model
The most important defects of Bohr’s theory :
- It failed to explain the spectrum of any other element, except the hydrogen atom, as it is considered the simplest electronic system which contains one electron only, even that of the helium atom contains only 2 electrons.
- It considered the electron as a negative charged particle only and ignored its wave properties.
- It postulated that it is possible to determine precisely both the location and speed of an electron at the same time, but in fact this is experimentally impossible.
- It described the electron as a particle moving in a circular planar orbit, which means that the hydrogen atom is planar, In fact, hydrogen atom has a spherical shape (three-dimensional coordinates).
Principle of modern atomic theory (modification of Bohr’s model):
The most important modifications are the following :
- The dual nature of the electron.
- The Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
- The wave-mechanical theory of the atom.
Dual nature of electron
The electron is a material particle that has wave properties: All the previously mentioned theories considered the electron just as a minute negatively charged particle, However, all experimental data showed that the electron has a dual nature, as it is a material particle that also has wave properties.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Bohr’s theory postulated that it is possible to determine both the location and velocity of the electron precisely at the same time, but by applying the principles of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg concluded that the determination of both the velocity and position of an electron at the same time is practically impossible, So, to speak in terms of probability seems to be more precise, This is because the electron wave motion does not have a certain location.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle: The determination of both the velocity and position of an electron at the same time is practically impossible and this is subjected to the laws of probability.
Wave-mechanical theory of the atom
The Austrian scientist Schrodinger (1926) applied the idea of Plank, Einstein, De Broglie and Heisenberg and could to:
- Establish the wave-mechanical theory of the atom.
- Derive a wave equation that could describe the electron wave motion in the atom.
On solving Schrodinger’s equation, it is possible to:
- Determine the allowed energy levels.
- Define the regions of space around the nucleus, where it is most probable to find the electron in each energy level.
The wave-mechanical theory changed our concept about the movement of the electron, where instead of speaking about the stable circular orbits as being completely forbidden for the electrons, the concept of the electron cloud is used to express the region of space around the nucleus.
The electron cloud is the region of space around the nucleus, in which the electron probable exists in all directions and distances (dimensions), There are regions inside the electron cloud in which the probability of finding the electron increases, each of them is termed by the orbital, Orbital is the region within the electron cloud of high probability of finding the electron.
Atoms components, Rutherford and Bohr’s Atomic Models
Evolution concept of the atomic structure, Atomic theory and Properties of cathode rays
The quantum numbers and principles of distributing electrons