Emergency Bleeding Management by Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab | Embolization Techniques
Emergency bleeding is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate diagnosis and rapid intervention. According to Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab, Consultant of Interventional Radiology, modern embolization techniques have dramatically changed the management of acute hemorrhage, providing safe and minimally invasive alternatives to surgery with excellent clinical outcomes.
What is Emergency Bleeding?
Emergency bleeding refers to an acute, uncontrolled hemorrhage that may arise from:
- Trauma and accidents.
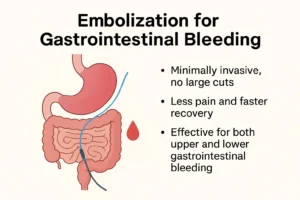
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Postoperative complications.
- Obstetric emergencies.
- Obstetric and gynecological emergencies.
- Tumors and vascular abnormalities.
Emergency bleeding may be classified into:
- External bleeding (visible hemorrhage).
- Internal bleeding (e.g., gastrointestinal, intracranial, retroperitoneal).
- Arterial or venous bleeding.
If not treated promptly, severe bleeding can lead to hypovolemic shock, organ failure, and death.
Role of Interventional Radiology in Emergency Bleeding
Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab emphasizes that interventional radiology (IR) plays a central role in controlling acute bleeding by accurately identifying the bleeding source and treating it using image-guided embolization. Interventional Radiology (IR) controls hemorrhage with minimally invasive techniques that can be lifesaving.
Interventional radiology (IR) plays a crucial role in the management of emergency bleeding. Using real-time imaging guidance such as fluoroscopy, CT, or ultrasound, interventional radiologists can accurately identify the bleeding source and treat it through transcatheter embolization.
Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab explains how emergency bleeding is managed using advanced embolization techniques in interventional radiology, with real clinical case studies.
Key advantages include:
- No surgical incision.
- Rapid bleeding control.
- Preservation of organ function.
- Shorter hospital stay.
- Suitable for critically ill or high-risk patients.
What Is Transcatheter Embolization?
Transcatheter embolization is a minimally invasive procedure in which a catheter is guided through blood vessels to the site of bleeding. An embolic agent is then injected to block the vessel and stop hemorrhage. According to Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab, embolization allows precise control of bleeding while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Embolization is a minimally invasive procedure in which embolic agents are introduced through a catheter to:
- Occlude bleeding vessels.
- Reduce blood flow.
- Achieve hemostasis.
Common Indications for Emergency Embolization
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Pelvic trauma hemorrhage.
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
- Hemoptysis.
- Tumor-related bleeding.
- Post-operative bleeding.
Different Embolization Techniques
1. Coil Embolization
- Metallic coils are used to occlude medium or large arteries.
- Indications: Trauma, gastrointestinal bleeding, aneurysms.
- Advantages: Permanent and highly precise occlusion.
2. Particle Embolization
- Microspheres or PVA particles are injected to block small vessels.
- Indications: Tumor-related bleeding, uterine bleeding.
- Advantages: Effective for diffuse hemorrhage.
3. Liquid Embolic Agents
- Includes NBCA (glue) and Onyx.
- Indications: High-flow bleeding, arteriovenous malformations.
- Advantages: Rapid and powerful vessel occlusion.
4. Gelfoam Embolization
- A temporary embolic agent that is gradually absorbed.
- Indications: Trauma and postoperative bleeding.
- Advantages: Temporary vessel occlusion with future recanalization.
5. Balloon-Assisted Embolization
- A balloon catheter is used to control blood flow during embolization.
- Indications: Large or complex vessel bleeding.
- Advantages: Increased procedural safety.
Steps of Emergency Embolization
- Vascular access (usually the femoral artery).
- Diagnostic angiography.
- Identification of bleeding source.
- Selection of embolic agent.
- Embolization.
- Post-procedure angiographic control.
Advantages of Embolization
- No large surgical incision.
- Local anesthesia.
- Short hospital stay.
- High success rate.
- Repeatable if needed.
Clinical Case Studies by Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab
Case 1: Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- A 65-year-old male presented with massive upper GI bleeding and shock. CT angiography showed active bleeding from the gastroduodenal artery.
- Treatment: Selective coil embolization.
- Outcome: Immediate bleeding control and full stabilization.
Case 2: Postpartum Hemorrhage
- A 32-year-old woman developed severe postpartum hemorrhage unresponsive to medical therapy.
- Treatment: Bilateral uterine artery embolization using particles and Gelfoam.
- Outcome: Bleeding stopped successfully with preservation of fertility.
Case 3: Pelvic Trauma Bleeding
- A 40-year-old male with pelvic fractures after a road traffic accident had ongoing internal bleeding.
- Treatment: Coil and Gelfoam embolization of internal iliac artery branches.
- Outcome: Hemodynamic stabilization without surgery.
Case 4: Tumor-Related Hemorrhage
- A patient with renal cell carcinoma developed spontaneous retroperitoneal bleeding.
- Treatment: Super-selective embolization using liquid embolic agents.
- Outcome: Immediate hemorrhage control and pain relief.
Safety and Complications
Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab confirms that embolization is a safe procedure when performed by experienced interventional radiologists.
Possible complications include:
- Post-embolization syndrome.
- Non-target embolization.
- Contrast reactions.
- Vessel spasm.
- Rare ischemic complications.
These are rare compared to surgical complications.
Emergency bleeding requires fast and effective treatment. According to Dr. Mahmoud Abdel Aziz Ghallab, embolization techniques represent the gold standard in many bleeding emergencies, offering life-saving results with minimal invasiveness. Interventional radiology continues to play a vital role in mod.
Emergency embolization is a cornerstone in modern bleeding management. Interventional radiology has transformed emergency care by offering fast, safe, and effective bleeding control.
Why Embolization Is Preferred in Emergency Bleeding
Embolization offers several advantages over surgical intervention:
- Minimally invasive procedure.
- Rapid identification and control of the bleeding source.
- Preservation of organ function.
- Reduced morbidity and mortality.
- Suitable for high-risk or unstable patients.
Book your consultation now!
📞 For bookings and inquiries: To contact Dr. Mahmoud Ghalab’s clinic or book an appointment:
- Address: 217 El Horreya Road (Abu Qir Street), Ibrahimia, GIG, International Center for Interventional Radiology
- Contact us by phone or WhatsApp 📍
- 01000113305
- 01000113305
- [email protected]
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
Common procedures of Interventional Radiology and the best Interventional Radiologists
Interventional radiology types, Robotic endovascular systems advantages and disadvantages
Cone beam CT vs. Fan beam CT, CBCT advantages, disadvantages and uses
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses, advantages and disadvantages
Computed Tomography (CT) types, uses, advantages and disadvantages
Artificial intelligence in radiology decision support systems, Medical Imaging and Healthcare
Enlarged prostate symptoms, Prostatic artery embolization (PAE) importance and risks
Hepatic Artery Embolization, Importance and risks of Embolization therapy for Liver cancer
Thyroid nodules, Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy importance and risks
Uterine fibroid embolization risks, importance and Minimally invasive procedure specialists