Importance and function of the mouth in the human digestive system
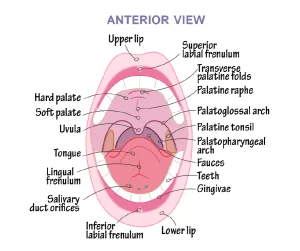
The mouth is the first organ in the digestive system, and it is a cavity in which the teeth and the tongue exist, and the salivary glands are opened, The function of the mouth is cutting and grinding the food by the teeth, and It digests the starch into the sugar.
Functions of the Mouth
The mouth plays a crucial role in both digestion and communication. The mouth, or oral cavity, is a complex organ with several essential functions:
Primary Functions
- Eating:
- Ingestion: Taking in food and liquids.
- Mastication: Chewing food into smaller pieces to aid digestion.
- Taste: Detecting flavors through taste buds.
- Swallowing: The mouth moves food from the mouth to the esophagus.
- Speaking: The mouth can form words and sounds by moving the lips, tongue, and teeth.
Secondary Functions
- Breathing: Although the nose is the primary airway, the mouth can also be used for breathing, especially during physical exertion or nasal congestion.
- Sensory Perception: The lips and tongue contain numerous nerve endings, providing sensations of touch, temperature, and pain.
The teeth
The number of teeth is 32 in adults, They exist in two jaws which are the upper jaw and the lower jaw, and each jaw has 16 teeth divided into 10 molars (4 premolars and 6 molars), four incisors, and two canines.
The function of the four incisors and two canines is cutting and tearing the food into small pieces, and the ten molars grind the food to make its swallowing easy.
The milk teeth are weak and formed through the childhood phase and their number is 20 teeth, where each jaw has ten teeth.
The milk teeth are completely replaced by strong ones before the age of twelve, and they are divided into 4 incisors, 2 canines, and 4 molars.
Tongue
The tongue is an organ that has several functions. It is the speech organ as it changes the sound coming from the larynx into understandable words.
The tongue mixes the food with the saliva to help in food swallowing, The tongue moves the food around inside the mouth cavity, and it is responsible for tasting the food.
Salivary glands
There are three pairs of salivary glands, they secrete saliva liquid that contains digestive substances (the enzymes) that digest the starch into the simple substances called sugar.
The enzymes are the digestive substances that digest the food and convert it into simple substances.
Importance of the Mouth
The mouth is a gateway to the body, influencing both our physical and social well-being. The mouth is a vital part of our body, serving multiple essential functions.
- Digestion: The process of breaking down food begins in the mouth. Chewing (mastication) helps in mixing food with saliva, which aids in swallowing and digestion.
- Communication: The mouth is essential for speech, allowing us to express ourselves and interact with others.
- Breathing: While primarily done through the nose, the mouth can also be used for breathing, especially during physical exertion or when the nasal passages are blocked.
- Taste: Our taste buds, located primarily on the tongue, enable us to experience the flavors of food and drinks.
Impact on Overall Health
- Oral Health: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing dental problems like cavities and gum disease.
- Systemic Health: Research suggests a link between oral health and overall health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Mouth Cavity divisions, anatomy, function, muscles, Contents of Soft palate and Hard palate
Digestion in man, Buccal digestion, and Gastric digestion (digestion in the Stomach)
Small intestine, Absorption of digested food, Metabolism, Large intestine and defecation
The function of the digestive system in the human body
Git function, Types of salivary secretion and Composition of saliva
Histological structure of salivary glands, Parotids, Sublingual and Submandibular glands
Norma lateralis features & anatomy, Mandible surfaces, nerves and ligaments
Tongue function, anatomy & structure, Types of lingual papillae and Types of cells in taste bud
Salivary glands function, shape, lobes, surfaces and Structures within the parotid gland