Metals and nonmetals, Economic importance of some metals and nonmetals
Every day, we can see the matter around us which has a mass and a volume. The matter may exist as an element or a compound, The element is the simplest form of matter that can not be analyzed into two substances or more. Elements are classified into metals, non-metals, and metalloids (semimetals).
 |
| There are 112 elements. |
Elements types
118 elements have been discovered up till now. and they are divided into natural elements (they are 92 elements) and artificial elements (they are 26 elements).
The elements are composed of small particles known as the molecules which are composed of atoms. Element molecules are formed of similar atoms that are different from those of the other elements.
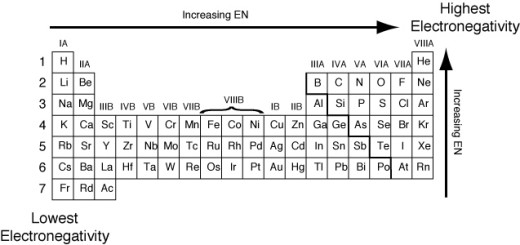
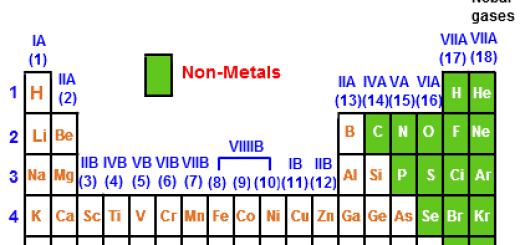
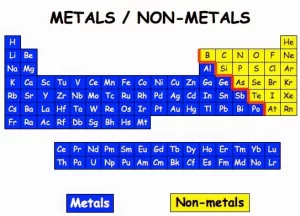
The scientists classified the elements according to their properties into metals,non-metals, and metalloids, Metals are placed on the left-hand side of the periodic table, and non-metals are on the right of the periodic table. The metalloids are intermediate in their properties, they are more like the nonmetals, but under certain circumstances.
Many metalloids can be made to conduct electricity, These semiconductors are used in computers and other electronic devices. Semimetals are also known as metalloids, All metalloids are solids, Metalloids can be shiny or dull, but have a metallic luster. Metalloids include Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Selenium, Arsenic, Antimony, and Tellurium.
Metals and nonmetals are two broad categories of elements with distinct physical and chemical properties. The economic importance of metals and nonmetals is undeniable. They are essential for the production of a wide range of goods and services, and they play a vital role in the global economy. They are the building blocks of our infrastructure, industries, and technologies.
Metals
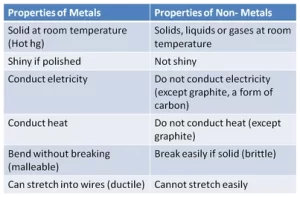
The metals are solids at room temperature, except mercury which is liquid. Solid metals such as copper, aluminium, lead, Iron, gold and silver. Metals are elements that form positive ions by losing electrons during chemical reactions, except hydrogen, they are electropositive elements with low ionization energies.
Most metals share the properties of being shiny, very dense, and having high melting points. Furthermore, they are ductile, malleable, and lustrous, Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Some metals will form a patina and the luster is lost. Gold is the most malleable of all the metals, Silver is one of the most ductile metals, Metals form cations in an aqueous solution by losing their electrons, Metals exhibit a wide range of densities but generally are denser than nonmetals. Tungsten, platinum, osmium, gold and iridium are extremely dense.
Metals are known for their good conductivity of heat and electricity, malleability (can be hammered into thin sheets), and ductility (can be drawn into wires). Due to these properties, metals have a wide range of applications in various industries.
Properties of metals
-
The metals are shiny. and they have metallic luster if they are pure.
-
They are good conductors of electricity.
-
They are good conductors of heat.
-
They have high melting and boiling points.
-
They can be bent, They are malleable, and they can be hammered to form sheets.
Non-metals
They are solids such as sulphur, carbon, and phosphorous. They are liquids such as bromine, and they are gases such as oxygenand nitrogen. Nonmetals form negative ions by gaining electrons during chemical reactions, so, they are electronegative elements with high ionization energies.
Nonmetals have poor conductivity of heat and electricity. They are also brittle and non-malleable. However, nonmetals are essential for various industries as well.
Properties of non-metals
-
They do not have a metallic luster, They are not shiny.
-
They are not malleable or they can not be hammered. They can not be bent.
-
They are bad conductors of heat.
-
They are bad conductors of electricity except for carbon.
-
They have low melting and boiling points.
Economic importance of some metals
- Iron is essential in making bridges, the car chassis (the car frames), the doors, and the sheet lights (The lamp posts), and it is metal. It is the most common metal on Earth. Iron is the primary component of steel, used in construction, transportation (cars, ships), machinery, and appliances.
- Copper is very important in making electric wires, statues and metallic coins, It is a metal. It is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity. It’s used in plumbing, roofing, and industrial machinery, and heat sinks for electronic devices.
- Gold is a precious metal used in jewelry, electronics, and as a financial asset.
- Silver is a precious metal with high electrical conductivity. It’s used in jewelry, electronics, and photography.
- Mercury metal is used in making thermometers.
- Aluminium is very important in the manufacture of cooking pans, foil paper, and some doorknobs, It is a metal, and it is a malleable metal. It is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it ideal for transportation (cars, airplanes) and packaging materials. It’s used in cans, airplanes, automobiles, and construction materials. It is a versatile metal with good conductivity.
Economic importance of some non-metals
- Silicon is the basic building block of semiconductors, which are essential components in computers, smartphones, and electronic devices.
- Nitrogen is a vital component of fertilizers, crucial for agriculture and food production.
- Natural Gas is a fossil fuel used for heating, cooking, industrial processes, and electricity generation.
- Phosphorus is a key ingredient in fertilizers, which are essential for agriculture and food production, It is used in detergents and fire retardants.
- Chlorine is used in water purification and the production of many industrial chemicals like PVC.
- Oxygen is the gas we breathe, also used in industrial processes like steelmaking and welding.
- Oil is a fossil fuel consisting of hydrocarbons, a major source of energy for transportation, energy generation, and industry.
- Carbon (graphite) is used in making the positive electrodes (The poles) of the dry batteries (the cells), and it is non-metal.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science Online Apps on Google Play