Metallic and nonmetallic property, Acidic and basic property in the periodic table
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Berzelius was the first scientist who classified elements into two main groups (metals and nonmetals), according to their physical properties, Indeed that was before knowing anything about atomic structure, This is an old classification which is still currently in use, although there are no boundaries between them and their properties in the periodic table.
With the development of our concept about the electron structure of atoms, we can differentiate between metals and nonmetals, Additionally, there is a third group of elements known as metalloids.
Metals
Their valence shell – generally – has less than half its capacity of electrons, They have large atomic radius which leads to small values for ionization energy and electron affinity.
They are electropositive elements, due to their tendency to lose electrons of the valence shell and change into positive ions to reach the structure of the nearest noble gas.
They are good electric conductors, due to the mobility of their few valence electrons, which can transfer from one position to another in the metal structure.
Nonmetals
Their valence shell – generally – has more than half its capacity of electrons, They have a small atomic radius which leads to high values for ionization energy and electron affinity.
They have small atomic radius which leads to high values for ionization energy and electron affinity, They are electronegative elements, due to their tendency to gain electrons to form negative ions that have the same electron structure of the nearest noble gas.
They do not conduct electricity (electric insulators), because their valence electrons are strongly bound to the nucleus, Thus, it is difficult for these valence electrons to be transferred.
Metalloids
The metalloids are characterized by the following properties:
They have the metallic appearance and the most properties of nonmetals, Their electronegativity is intermediate between metals and nonmetals, Their electric conductivity is less than that of metals but more than that of nonmetals, They are used in manufacturing electronic instruments parts – such as transistors – as they are semiconductors.
Metalloids are a group of elements that have a metallic appearance and most of the properties of nonmetals which characterized by their electronegativity is intermediate between metals and nonmetals and their electric conductivity is less than that of metals, but more than that of nonmetals.
The graduation of metallic and nonmetallic properties in the periodic table:
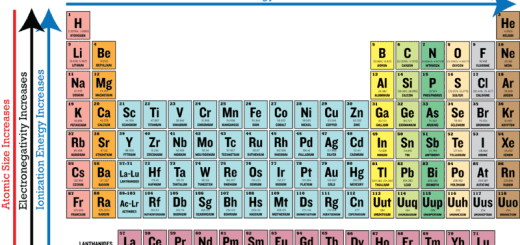
In the same group: The metallic character increases (The nonmetallic character decreases) with the increase in the atomic number as we go down the group, due to their large atomic radius and the low ionization potential and electron affinity.
In the same period: The period begins with the strongest metals in group 1A, then the metallic property decreases gradually by increasing the atomic number across the period till we reach the metalloids, To the right of the metalloids begins the nonmetallic property, The period ends by the elements of the highest nonmetallic property in group 7A.
Consequently: Cesium is considered the most active metal because the metallic property increases in the same group by increasing the atomic number and it is placed at the bottom of the left-hand side of the table (the lowest metal in ionization potential).
Fluorine is considered the most active nonmetal because the nonmetallic property decreases at the same group by increasing the atomic number and it is placed at the top of the right side of the table (the most electronegative nonmetal).
The graduation of metallic and nonmetallic properties in the third period, It is clear that by increasing the atomic number, the metallic character decreases and the nonmetallic character increases.
Acidic and basic property
When an element combines with oxygen forming a compound known as oxide, There are types of element oxides which are Acidic oxides, Basic oxides, and Amphoteric oxides.
Acidic oxides
The nonmetallic oxides are named by acidic oxides, because:
They dissolve in water forming oxygenated acids.
CO2 ( g ) + H2O ( l ) → H2CO3 ( aq )
SO3 ( g ) + H2O ( l ) → H2SO4 ( aq )
They react with alkalis forming salt and water.
CO2 ( g ) + 2NaOH ( aq ) → Na2CO3 ( aq ) + H2O ( l )
From the acidic oxides, Carbon dioxide CO2, Sulphur trioxide SO3, and Nitrogen dioxide NO2.
Basic oxides
The metallic oxides are usually known as basic oxides, Some basic oxides are not soluble in water and others are soluble in water forming alkalis, the water soluble basic oxides are also known as alkali oxides.
K2O ( s ) + H2O ( l ) → 2KOH ( aq )
H2O ( l ) + Na2O ( s ) → 2NaOH ( aq )
From the basic oxides, Potassium oxide K2O, Sodium oxide Na2O, Magnesium oxide MgO.
They react with acids forming salt and water:
2HCl ( aq ) + Na2O ( s ) → 2NaCl ( aq ) + H2O ( l )
MgO ( s ) + H2SO4 ( aq )→ MgSO4 ( aq ) + H2O ( l )
Amphoteric oxides
Amphoteric oxides are element oxides that react with acids as basic oxides and react with bases as acidic oxides forming in both cases salt and water.
ZnO ( s ) + H2SO4 ( aq )→ ZnSO4 ( aq ) + H2O ( l )
ZnO ( s ) + 2NaOH ( aq )→ Na2ZnO2 ( aq ) + H2O ( l )
Amphoteric oxides such as Aluminum oxide Al2O3, Zinc oxide ZnO, Antimony oxide Sb2O3, and Tin oxide SnO.
The graduation of acidic and basic properties in the periodic table
In the period: The basic property of the oxide decreases as the atomic number of the element increases, while the acidic property increases.
In the group: where in the group that starts by a metal, the basic property of the oxide increases as the atomic number increases as in group 1A.
In the group that starts with a nonmetal, The acidic property of the oxide increases as the atomic number increases as in group 7A.
The graduation of acidic and basic property in the third period, As the atomic number increases the basic property decreases and the acidic property increases.
The acidic property of hydrogen compounds of group 17 (halogens) increases as the atomic number increases Because the increase in the atomic number in the group leads to the increase in the atomic size of halogen and then its attraction force for hydrogen atom decreases, making it easier to be ionized.
Radius property, Ionization potential, Electron affinity and Electronegativity
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Hydroxy compounds, Rules for calculating the oxidation numbers